اتفاقية الشراكة الاقتصادية الشاملة بين الإمارات وماليزيا
تعرف على
اتفاقية الشراكة الاقتصادية الشاملة بين الإمارات وماليزيا
تعزز الاتفاقية من متانة العلاقات الاقتصادية بين الإمارات وماليزيا، وتهدف إلى تعميق التعاون في عدد من القطاعات الرئيسية، وتعزيز سلاسل التزويد، وتمكين الاستثمارات، وبما يسهم في فتح آفاق جديدة لازدهار القطاع الخاص في البلدين.
وللاتفاقية قيمة استراتيجية كبيرة لكلا البلدين، إذ توفر مدخلاً إلى تكتلات اقتصادية أوسع. حيث من المتوقع أن تعزز مكانة الإمارات كمركز استراتيجي للصادرات الماليزية إلى منطقة الشرق الأوسط وشمال إفريقيا وأبعد، في حين تفتح أسواق جنوب شرق آسيا أمام التجار ورواد الأعمال والمستثمرين الإماراتيين.
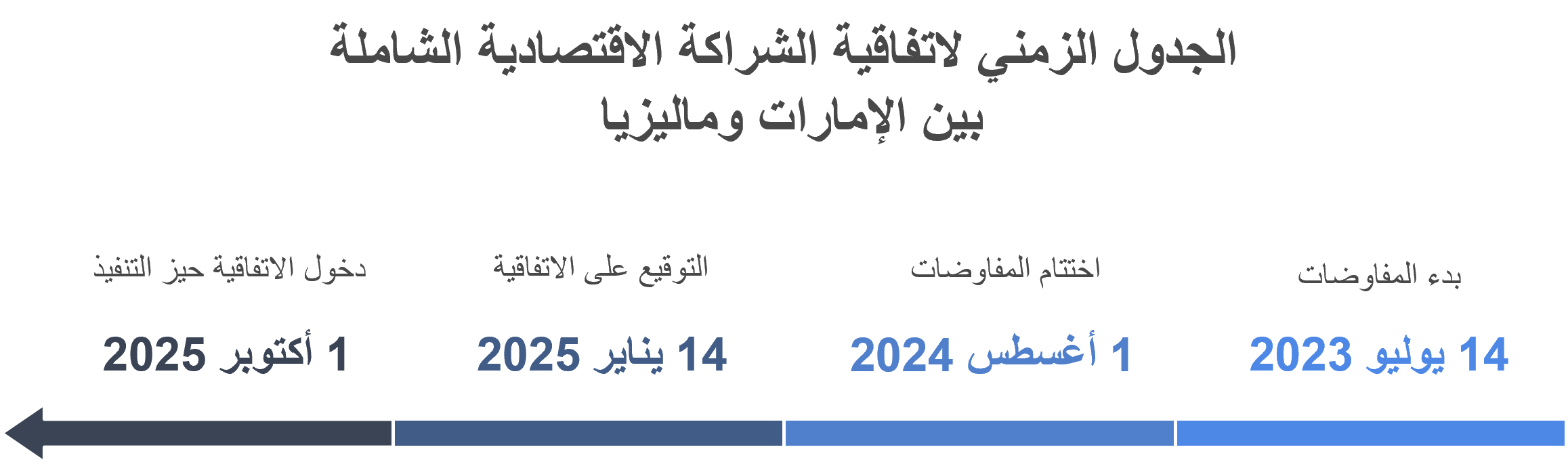
جدول زمني
لمحة
وُقِّعت اتفاقية الشراكة الاقتصادية الشاملة بين الإمارات وماليزيا في أبوظبي بتاريخ 14 يناير 2025، من قبل معالي الدكتور ثاني بن أحمد الزيودي، وزير التجارة الخارجية الإماراتي، ومعالي تنكو زفرول عزيز، وزير الاستثمار والتجارة والصناعة في ماليزيا.
جرت مراسم التوقيع تحت رعاية صاحب السمو الشيخ محمد بن زايد آل نهيان، رئيس دولة الإمارات، ودولة أنور إبراهيم، رئيس وزراء ماليزيا.
المجالات التي تشملها الاتفاقية
تتكون اتفاقية الشراكة الاقتصادية الشاملة بين الإمارات وماليزيا من 19 فصلًا وملاحقها. وتوفر الاتفاقية إمكانية الوصول إلى الأسواق للسلع؛ وتنص على إزالة أو خفض الرسوم الجمركية على معظم السلع؛ وتضم التزامات بشأن الحواجز غير الجمركية، وتحرير تجارة الخدمات، وفتح مسارات جديدة للاستثمار، وتعزيز التعاون بين الشريكين، وغير ذلك.
ملخص للموضوعات التي تتضمنها الاتفاقية
التجارة في السلع
تتضمن اتفاقية الشراكة الاقتصادية الشاملة بين الإمارات وماليزيا على الإلغاء الفوري للتعرفة الجمركية على معظم السلع المؤهلة المنتجة في ماليزيا أو دولة الإمارات، بما في ذلك تلك القادمة من المناطق الحرة. وأما باقي المنتجات فقد تخضع إلى انخفاض تدريجي للتعرفة الجمركية خلال فترة 7 سنوات بالنسبة لماليزيا و5 سنوات بالنسبة للإمارات أو وفق حصص كمية محددة. كما أن هنالك عدداً من السلع الحساسة والممنوعة والتي تم استثنائها من المعاملة التفضيلية.
للحصول على معلومات تفصيلية حول التعرفة الجمركية التفضيلية، يُرجى الاطلاع على لوحة البيانات الخاصة بالاتفاقية عبر الرابط أدناه.
ولكي تستفيد السلع من المعاملة الجمركية التفضيلية، يجب أن تستوفي متطلبات قواعد المنشأ التي تتميز بالمرونة وتهدف إلى تعزيز التجارة المتبادلة بين الشريكين. كما تدعم الاتفاقية انسياب السلع بطريقة مبسطة وأقل تكلفة وفي الوقت المناسب من خلال ترتيبات تيسير التجارة والتعاون الجمركي.
كما تضع الاتفاقية قواعد تضمن توافق متطلبات الصحة والسلامة للمنتجات مع المعايير الدولية وعدم تحولها إلى عوائق أمام التجارة.
وتعزز الاتفاقية مبدأ التجارة العادلة من خلال السماح باتخاذ تدابير مؤقتة لمواجهة الممارسات التجارية غير العادلة أو الارتفاع المفاجئ في الواردات، وذلك بما يتماشى مع اتفاقيات منظمة التجارة العالمية المتعلقة بإجراءات الوقاية والدعم والرسوم التعويضية وتدابير مكافحة الإغراق، إضافة إلى السماح باتخاذ تدابير وقائية ثنائية.
التجارة في الخدمات
تضع الاتفاقية قواعد واضحة وشفافة لتيسير توريد الخدمات عبر الحدود وضمان تمتع مزوّدي الخدمات بمعاملة مميزة في قطاعات وخدمات فرعية متعددة، مثل الخدمات المهنية، والخدمات المالية، والخدمات اللوجستية، والسفر والسياحة، وخدمات النقل.
للحصول على تفاصيل إضافية، يُرجى الاطلاع على فصل التجارة في الخدمات وملاحقه الخاصة بجداول الالتزامات المحددة التي تشمل القطاعات والخدمات الفرعية عبر الرابط أدناه.
التجارة الرقمية
تضع الاتفاقية قواعد مشتركة لتعزيز الثقة في مجال التجارة الرقمية المتطور باستمرار، والذي أصبح عنصراً أساسياً في الاقتصاد العالمي الحديث. حيث تسهم هذه القواعد في تعزيز الثقة وتضمن استفادة الشركات والمستهلكين على حد سواء من تدفقات التجارة الرقمية.
تيسير الاستثمار
تؤكد الاتفاقية التزام كل طرف بحماية الاستثمار بموجب معاهدة الاستثمار الثنائية الموقعة عام 1991، كما تنص على إنشاء مجلس فني لتعزيز تدفقات الاستثمار، وتحديد الفرص لتوسيع الاستثمارات، والتغلب على العقبات الاستثمارية، والتواصل مع مجتمع الأعمال.
المشتريات الحكومية
تنشئ الاتفاقية نقاط اتصال وآلية لتعزيز الشفافية وتتيح للطرفين التجاريين التعاون في مجال المشتريات الحكومية.
حقوق الملكية الفكرية
تؤكد الاتفاقية على المبادئ والمعايير الدولية القائمة فيما يتعلق بحماية وإنفاذ حقوق الملكية الفكرية مما يسلهم في دعم الاختراع والابتكار والإبداع.
المؤسسات الصغيرة ومتوسطة الحجم
نظراً إلى المتطلبات الخاصة التي تحتاجها المؤسسات الصغيرة والمتوسطة الحجم لتمكينها من الانخراط بالتجارة العالمية فقد تضمنت الاتفاقية مجموعة من الالتزامات منها توفير المعلومات ووضع منصات مشتركة تساعد هذه المؤسسات على بناء الروابط وتعزيز قدراتها وذلك للتسهيل على هذه المؤسسات ومساندتها في الاستفادة من مزايا الاتفاقية من أجل نمو أعمالها وجذب الاستثمارات.
التعاون الاقتصادي
تعزز الاتفاقية التعاون والتنسيق بين الشريكين لدعم روابط اقتصادية أقوى وضمان استفادة القطاع الخاص بشكل كامل من الفرص التي تتيحها الاتفاقية. وتشمل مجالات التعاون الصناعات التحويلية؛ الزراعة والغابات ومصايد الأسماك؛ السياحة؛ الطاقة؛ سلاسل القيمة العالمية؛ تعزيز التجارة والاستثمار؛ الملكية الفكرية؛ تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات؛ بناء القدرات والمساعدة الفنية؛ والمنافسة، إضافةً إلى المؤسسات الصغيرة والمتوسطة. كما يمكن للشريكين الاتفاق على مجالات تعاون جديدة أخرى تخدم مصالحهما المشتركة وتسهم في تحقيق أهداف الاتفاقية .
الاقتصاد الإسلامي
تتضمن الاتفاقية بنودًا تشجع التعاون بين الشريكين لتطوير الاقتصاد الإسلامي في مجالات مثل المنتجات الحلال والخدمات المالية والسياحة.
تسوية النزاعات التجارية
تؤكد آلية تسوية المنازعات التجارية بين الدول على التزام الشريكين بحل الخلافات ضمن مدد زمنية محددة وبما يكفل مستويات تحرير التجارة المتفق عليها ويخدم نمو الاقتصاد.
إدارة الاتفاقية
تنشئ اتفاقية الشراكة الاقتصادية الشاملة هيكل مؤسسي يتألف بشكل رئيسي من لجان ولجان فرعية متخصصة تتولى إدارة ومتابعة تنفيذ مختلف جوانب الاتفاقية.
تشمل اتفاقية الشراكة الاقتصادية الشاملة بين الإمارات وماليزيا 19 فصلاً
كتيب اتفاقية الشراكة الاقتصادية الشاملة بين الإمارات وماليزيا
سيتم مشاركة الكتيب قريباً
لوحة بيانات - نفاذية اتفاقية الشراكة الاقتصادية الشاملة بين الإمارات وماليزيا إلى الأسواق
يمكن الآن للمصدرين من دولة الإمارات الاستفادة من زيادة الوصول إلى الأسواق من خلال معدلات رسوم جمركية تفضيلية. تخضع بعض المنتجات لرسوم جمركية صفرية بدايةً من اليوم الأول، بينما تشهد بعض المنتجات الأخرى تخفيضات للرسوم الجمركية بمرور الوقت. لتحديد تصنيف التعرفة الجمركية (الكود الخاص بمنتجك)، راجع لوحة التحكم وابحث عن الوصف الذي يمثل منتجك على أفضل وجه وستجد كود منتجك في الجدول المخصص، وبما يمكنك عرض معدل التعرفة التفضيلية لمنتجك وتقدير الرسوم




